1Learning Outcomes¶
Practice loads and stores.
Translate array accesses in C code into assembly instructions (see Long Example).
No video. We recommend pulling up the memory section of the RISC-V Green Card.
2Example 1¶
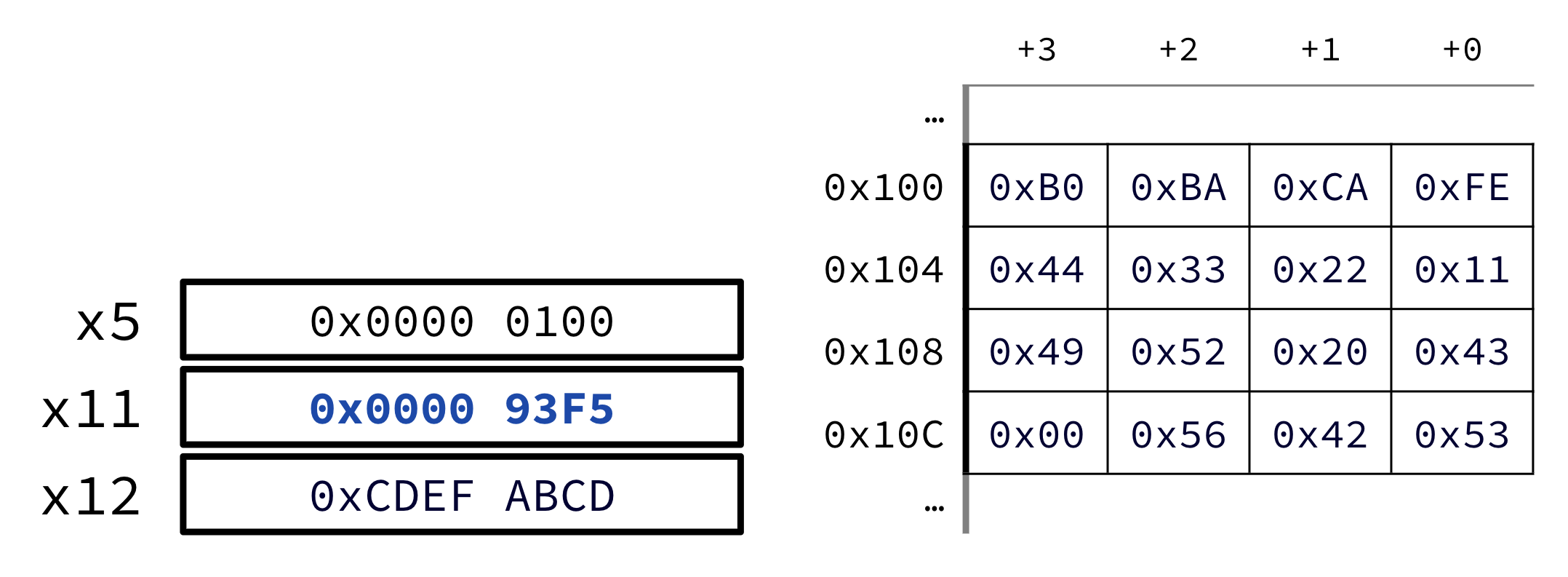
Consider the assembly code:
li x11 0x93F5
sw x11 0(x5)
lb x12 1(x5)Suppose that the memory layout starts as in Figure 1. After executing these instructions, what is in x12?
Hint: See the section on pseudoinstructions like li.
Show Answer
R[x12] is 0xFFFF FF93.
Explain li x11 0x93F5
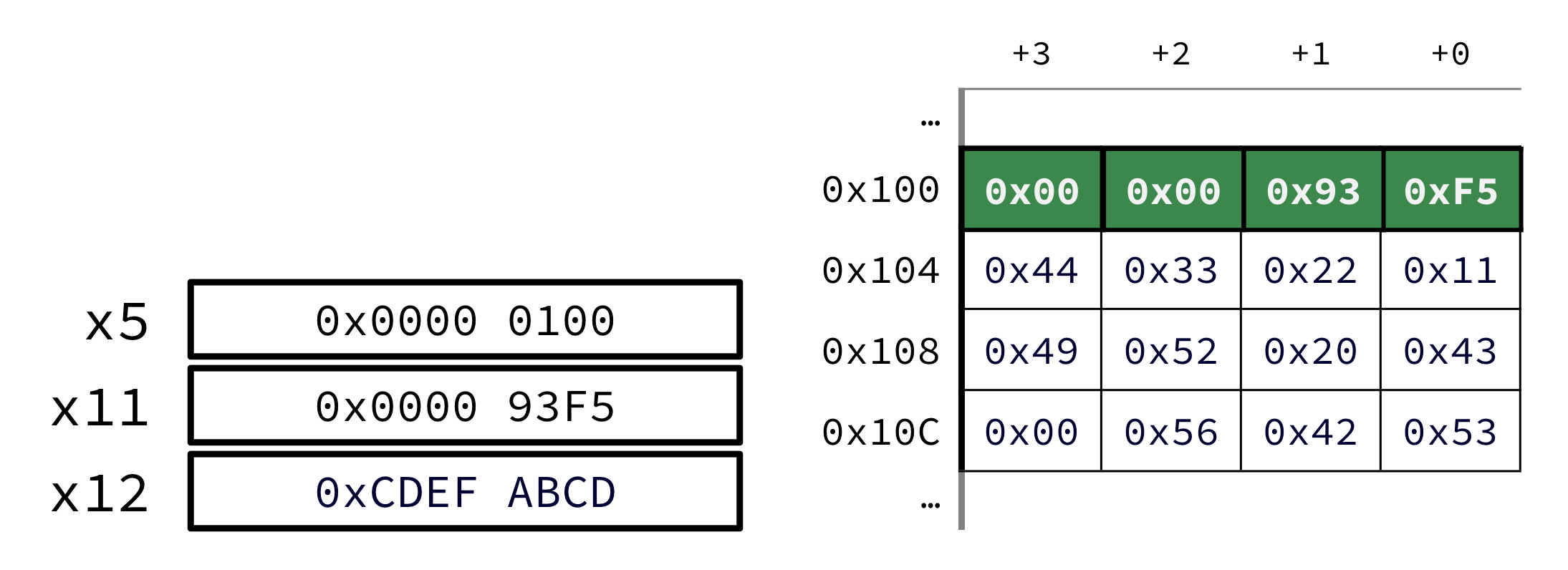
li x11 0x93F5Explain sw x11 0(x5)
sw x11 0(x5)Explain lb x12 1(x5)
lb x12 1(x5)Compute memory address as base register + offset, or R[x5] + 1 = 0x100 + 1 = 0x101. Load byte 0x93 from memory at address 0x101 into the lowest byte of register x11.
lb means we must sign-extend. The top bit of 0x93 is 1, so fill top 24 bits with 1s:
0x93 = 0b1001 0011
--> 0b1…1 1001 0011
--> 0xFFFF FF93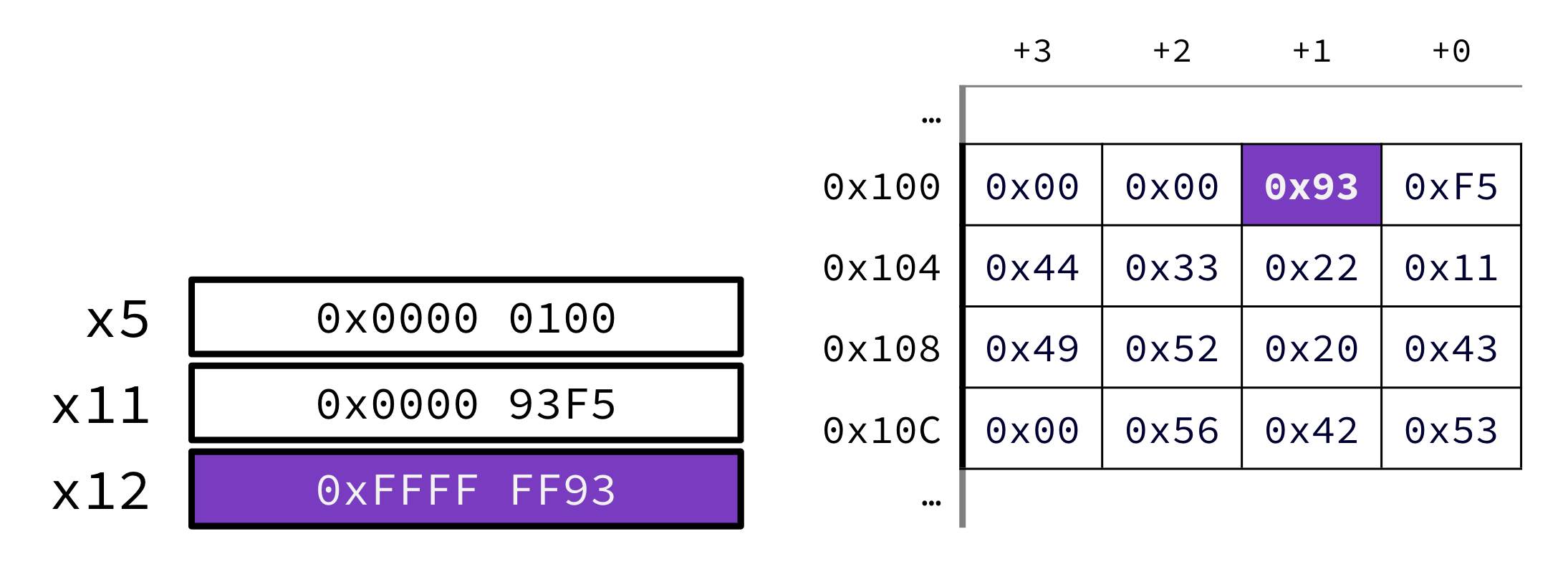
Solution: R[x11] (the value in x11) is 0xFFFFFF93.
2.1Example 2¶
Suppose that x and y are int * pointers whose values are in registers x3 and x5.
How do we translate the statement *x = *y; into assembly?
Consider the following instructions:
add x3 x5 zero
add x5 x3 zero
lw x3 0(x5)
lw x5 0(x3)
lw x8 0(x5)
sw x8 0(x3)
lw x5 0(x8)
sw x3 0(x8)
And consider the following choices:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5 → 6
F. 6 -> 5
G. 7 → 8
H. Something else